- Kartaltepe Mahallesi İncirli Caddesi Limon Çiçeği Sokak No: 1 34145 Bakırköy İstanbul
- +90 541 548 52 47
Hair loss or alopecia in the terminology; It is a problem with sociological, psychological and medical dimensions. Existing and traditional medical interventions may not always be sufficient for this problem, which can be caused by many factors. For this reason, various therapeutic approaches are being investigated in regenerative medicine for the treatment of alopecia . Evidence is sought on the efficacy of potential treatment options, such as stem cell implantation or platelet- rich plasma. So, what is the most promising regenerative treatment for alopecia ? The results of scientific studies and clinical studies are not yet sufficient to give a clear answer to this question. Although regenerative treatment approaches offer promising results in the treatment of certain types of alopecia , more evidence is needed for firm statements.
What is the Function of Hair in Our Body?
Hair, located in various parts of our body, performs many important functions. They have critical roles such as protection of the body against external factors, heat insulation, oil secretion and camouflage . Non-physical conditions such as emotional perception and social interaction, that is, the psychological function, should not be ignored. The hair follicle is subject to a dynamic and complex growth cycle that changes in 3 phases. The catagen phase, which is characterized as the transition period, is followed by the phase , which we call the anagen phase , in which rapid growth occurs . The process in which the hair becomes thinner and hair growth stops is called the telogen phase. Conditions such as stress, trauma , pregnancy or nutritional deficiency can accelerate the transition of hair to the telogen phase.
How Many Types of Alopecia Are There?
We can talk about many types of hair loss or alopecia . However, alopecia is basically; cicatricial It is divided into two subtypes, alopecia and non -cicatricial alopecia . According to researches; cicatricial alopecia accounts for 5% of all alopecia cases. Androgenetic, known as genetic predisposition hair loss alopecia, which is thought to be triggered by alopecia and autoimmune diseases and known as ringworm alopecia types such as areata ; It is in the category of non -cicatricial alopecia.
Can Alopecia Be Stopped With Pharmacological Treatment?
The methods used in the treatment of alopecia vary according to the type and severity of alopecia . There are several pharmacological treatment options that have been approved by regulatory agencies such as FDA and EMA for their safety, efficacy, and clinical use. Treatments containing 5α-reductase inhibitors such as minoxidil and Finasteride can be effective in preventing some types of alopecia or slowing the hair loss process.
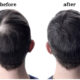
How Effective is Regenerative Medicine in the Treatment of Alopecia?
Regenerative medicine; cells, tissues and organs; It includes treatment approaches aimed at repairing, changing and renewing. Evidence-based regenerative medicine reports show that various therapeutic practices improve hair follicles and increase their functionality . Regenerative approaches consist of treatments that provide healing at the cellular level, such as stem cells and platelet- rich plasma, abbreviated as PRP. We are not strangers to the application of stem cell and PRP treatments for anti- aging purposes. In the fight against the problem of hair loss, we frequently encounter them as popular treatment options in recent years. Scientists are of the opinion that the evidence networks should be further expanded for clear statements about the effectiveness of regenerative medicine approaches on cases of alopecia .
In conclusion,
There is no single cause of hair loss, and there is no single treatment option to solve this problem. In addition, no option is certain and permanent, regardless of the treatment method. Studies so far show that certain types of hair loss can be controlled with regenerative medicine strategies. Applications such as stem cells and PRP are promising both in the treatment of some diseases and in the fight against hair loss.