- Kartaltepe Mahallesi İncirli Caddesi Limon Çiçeği Sokak No: 1 34145 Bakırköy İstanbul
- +90 541 548 52 47
Botched hair transplant: 5 Main Reasons and Top Tips to Avoid Them
27/09/2022
Everything you need to know about infection after hair transplant
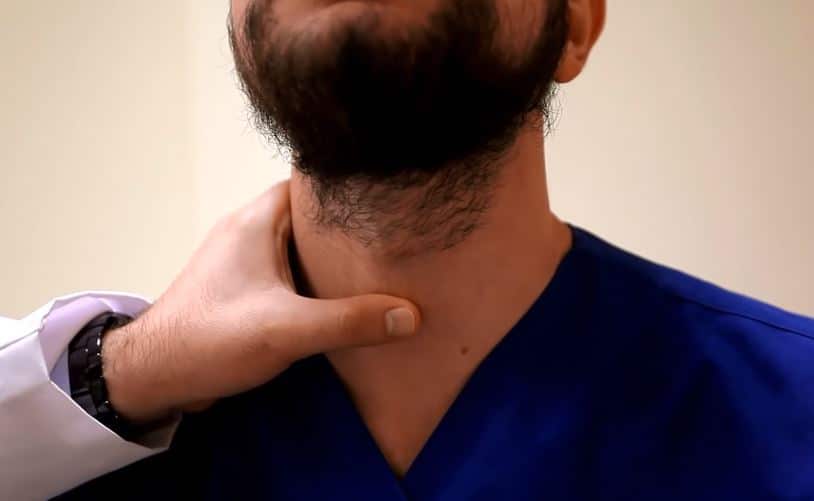
27/09/2022Thyroid disorders are closely related to hair loss. This butterfly-shaped organ is located at the front of the neck and is responsible for the production of hormones called triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). It is responsible for controlling our basal metabolic rate, hair growth, body temperature, muscle tension, nervous growth, reproduction, skin homeostasis, as well as our intelligence.
No one can deny that hair loss negatively affects a person’s life. Everyone has a different experience. It can also be financially challenging for someone who is starting to look for products to heal or even hide different hair health issues. Hair loss can occur if thyroid hormones are not properly balanced. Although iodine deficiency has been exaggerated as the cause of this problem, there are many other causes as well, such as pregnancy, age, gender, medications, and genes.
Hyperthyroidism affects 5 out of every 1000 women, and hypothyroidism affects 3 out of every 1000 women. Yes, it is more common in women. If this disease rises while pregnant, it is very risky because it has been determined that it can cause premature birth, death of the fetus, stillbirth and harm the neuropsychological development of the baby.
There are two major classifications of thyroid problem.
1. Hypothyroidism
2. Hyperthyroidism
hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, also called active thyroid, is the problem of the patient’s thyroid gland not producing enough hormones.
Hypothyroidism may not cause obvious symptoms in the early stages. If hypothyroidism is not treated over time, it can cause some health problems such as weight gain, fatigue, lethargy, constipation, hair loss.
hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism happens when you produce too much of T4, T3, or both. Detecting an overactive thyroid and treating the root cause can alleviate the indications and stop the problems.
Thyroid Disease – Hair Loss Relationship
Severe and long-term hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause hair loss. The loss spreads and can take over the entire scalp rather than some parts. Hair thins. If the treatment of the thyroid disorder is successful, regrowth can occur. But that doesn’t happen right away.
Hair loss due to thyroid disease occurs a few months after the onset of thyroid disease. This occurs due to the long hair cycle. In such cases, hair loss may occur after the procedure or treatment for the thyroid, and sometimes thyroid medications are mistakenly blamed, leading to discontinuation of the treatment, possibly worsening the hair loss.
It is not normal for thyroid problems to cause hair loss with no other signs of an overactive or underactive thyroid. Your doctor will determine if it is appropriate for you to have extra tests to rule out other causes of hair loss, such as iron deficiency. Sometimes you may need to be referred to a skin specialist to reach the correct diagnosis.
Thyroid and Hair Loss Treatment
Do not delay and see a doctor. Do not self-diagnose for hair loss. Many people think that a healthy diet will solve this problem, but the thing is, it is completely wrong. You need to know the cause of hair loss. Then you can find the right solution to fix the problem.
Is Hair Transplantation Necessary for Thyroid Patients?
The seriousness of the problem may be the answer to this question. Hair loss due to thyroid disease is usually short-lived. However, if this bothers you too much, you can go to a clinic and decide after a consultation whether you really need a hair transplant. In addition, non-severe cases usually do not require large-scale intervention for hair transplantation. However, finding the right treatment is key so that the damage isn’t permanent. If thyroid disease has taken a toll on your hair growth, a hair transplant is a possibility and the results can be great too.